Probiotics are an excellent choice and means to maintain and promote our health. Their use brings a number of benefits to various systems in the body, foremost among them the digestive and immune systems. They contribute to the maintenance of vital tone and general health.
The quality of the products themselves is of great importance for the action and effectiveness of probiotics. It is important which probiotic strains are included in the products and whether they can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach until they reach the intestines, where their site of action is. It also matters whether the probiotic bacteria are capable of forming viable colonies and whether this ability is maintained throughout the shelf life, not just at the date of manufacture. On these parameters, not all probiotics on the market are the same.
Nature's Way Primadophilus range have been developed with these principles, requirements and standards in mind to ensure the highest possible quality and deliver the desired effect.
Contains a proprietary blend of 3 probiotic strains (Lactobacillus reuteri (UALre-16), Lactobacillus acidophilus (DDS-1), Lactobacillus rhamnosus (HN001)) as well as a proprietary prebiotic blend of fructooligosaccharides (NutraFlora ® scFOS).
Lactobacillus acidophilus is among the best-studied probiotic bacteria. L. acidophilus has been shown to successfully colonize the colon, where it exerts positive effects. First of all, by releasing lactic acid, the multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms is inhibited. It has also been found to increase the number of another type of beneficial bacteria, Bifidobacteria. Another benefit is that they increase the amount of butyrate (a short-chain amino acid responsible for breaking down fibre) secreted into the gut. Butyrate also plays another role. It favours the natural barrier function of the intestine, thereby reducing the possibility of pathogenic micro-organisms and their secretions entering the central circulation and leading to inflammation and infection.
A number of studies have demonstrated the ability of L. acidophilus to affect diarrhea, including antibiotic-induced diarrhea. It has been shown to inhibit colonization of the intestine by the pathogenic microorganism Clostridium difficile, which can lead to the severe condition pseudomembranous colitis, which is a side effect of certain groups of antibiotics. In addition, evidence suggests that L. acidophilus may also beneficially affect diarrhea following radiotherapy (Imjai Chitapanarux et al., 2010).
Lactobacillus rhamnosus is another popular strain of lactic acid probiotic bacteria. In addition to the above effects, it has also been found to be capable of inhibiting the growth of the pathogenic microorganism Helicobacter pilori. H. pilori is believed to be the main causative agent of gastric and duodenal ulcers. L. rhamnosus not only inhibits the multiplication of the pathogenic microorganism, but also secretes factors favouring the functioning and repair of the protective mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
The combination of L. acidiphilus and L. rhamnosus has been found to have a beneficial effect on the immune system at the local (in the gastrointestinal tract itself) and systemic level. Among the benefits found are influencing irritable bowel syndrome, allergies, atopic dermatitis, and others, by modulating the immune response and the expression of certain genes in the gastrointestinal tract that influence these conditions (Julio Plaza-Diaz et al, 2014).
A more unusual probiotic strain, Lactobacillus reuteri, is also included in the composition of Primadophilus Reuteri. Current studies over it have shown anti-inflammatory activity and beneficial effects on blood cholesterol levels. Daily supplementation with L. reuteri has been shown to reduce cardiovascular events (so far confirmed in experimental animals) by influencing inflammation and hypercholesterolemia. The mechanisms by which this occurs may be diverse, and so far the effect is thought to be due to regulation of enzymes responsible for cholesterol metabolism, direct binding and efflux via the feces, inhibition of synthesis, and others.
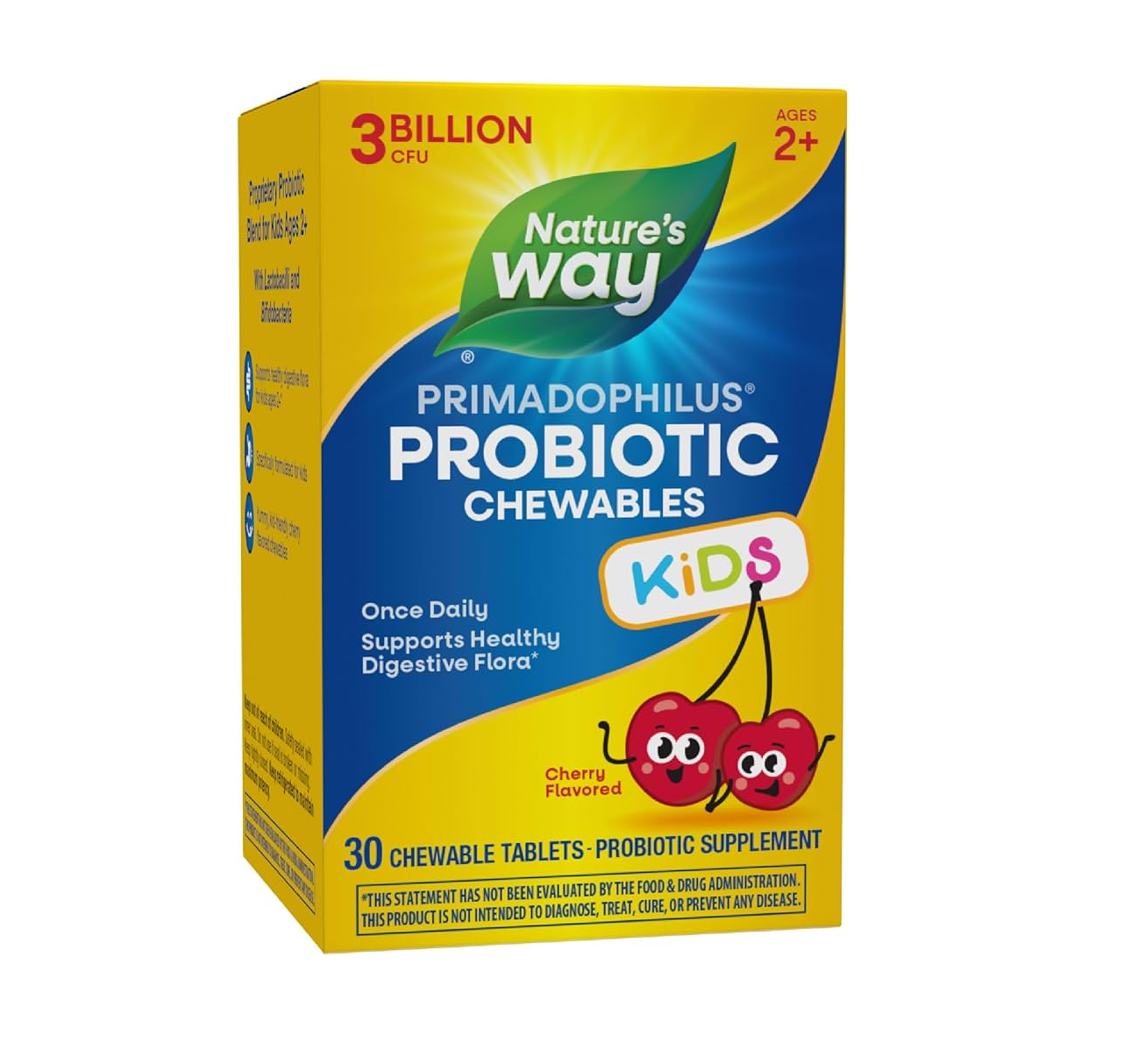
Developed to meet the needs of children between the ages of 2 and 12. It contains Lactobacillus plantarum (Lp-115®), Bifidobacterium bifidum/lactus (Bb-02), Lactobacillus acidophilus (La-14®).
Lactobacillus plantarum may influence the optimal absorption of beneficial food constituents and exert an antioxidant effect. In animal experiments, it has been found that they can exert beneficial effects against inflammation and optimize blood sugar levels by affecting insulin sensitivity (Hyun Seong Youn et al, 2021).
Bifidobacteria can also be mentioned to mediate the immune response, promote gastrointestinal health, limit the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and furthermore promote the growth and attachment of probiotics by promoting the barrier effect of the intestinal mucosa.
These properties make Primadophilus Kids particularly suitable for the growing children's organism. It finds application for dealing with gastrointestinal problems such as bloating, gas, upset stomach, diarrhea, including when using antibiotics. It promotes proper absorption of substances from food and supports the child's immune system, not only in infections, but also in conditions such as allergies, eczema and others.
NutraFlora® scFOS prebiotic blend contains short-chain fructooligosaccharides. These co-sediments are of natural origin and accelerate the colonization of the intestinal mucosa by lactobacilli. They are water-soluble fibres that serve as "food" for the probiotics, thus ensuring their successful uptake and multiplication.
The Primadophilus series has certifications for defined probiotic strains - True Identity™ - only the specified strains are included in the product, True Release™ - confirms the survival of probiotics in the aggressive conditions of acids and juices in the stomach and small intestine and True Potency™ - guarantees the activity and number of colony forming units until the expiry date, not only at the time of production.
Probiotics have been proven safe with long and prolonged intake. It has been shown that even intake over months does not pose health risks and dangers, quite the contrary. This helps to fully develop the effects of the products and achieve their benefits. Daily intake guarantees their action.
It is advisable to ingest probiotics on an empty stomach. This will mean an hour or two after the last meal or 30 minutes before any food intake. During antibiotic therapy, they should be taken at least 1-2 hours apart from the antibiotic intake. This ensures that neither the antibiotic therapy nor the effects of probiotics are compromised.