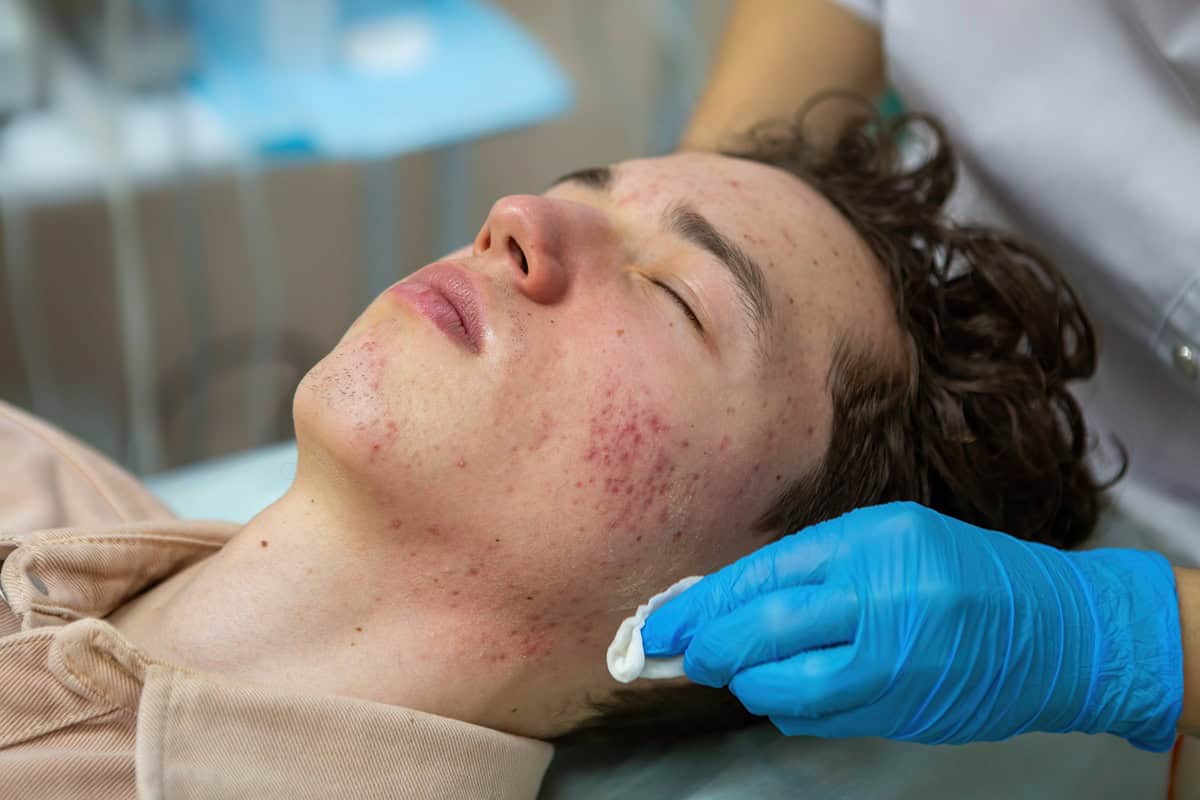
Acne is a skin condition that primarily affects the face. It is characterized by the appearance of pimples, which can negatively impact your self-esteem and quality of life.
If you're interested in learning more about this condition, we encourage you to read the article to the end. We’ll explore what acne is, the different types, its causes, main symptoms, and how to effectively treat it.
What is Acne?
Acne is a condition that arises as a result of an inflammatory process. It occurs when the skin's pores become clogged due to the excessive production of sebum and the infiltration of bacteria. This leads to the formation of pimples, most commonly on the face, but it can also affect other areas such as the neck, shoulders, chest, and back.
In addition to pimples, acne can also cause scarring, discoloration, and redness. In some cases, it may be confused with rosacea, as both conditions share similar symptoms.
Types of Acne
Acne can be classified into three types: retentional, inflammatory, and cystic acne.
Retentional Acne
Retentional acne is usually the first sign that something is wrong with the skin. In this case, areas like the forehead, nose, cheeks, and chin become oily, and the pores visibly enlarge. Blackheads and microcysts may also appear.
Inflammatory Acne
Inflammatory acne is caused by the overgrowth of the bacterium Cutibacterium acnes, which thrives in sebum. This type is marked by the appearance of red, often painful pimples called papules. Symptoms may subside temporarily and then return.
Cystic Acne
Cystic acne is the most severe form of the condition. The pores become blocked with sebum and bacteria, leading to the development of painful cysts beneath the skin’s surface. If not properly treated, these cysts can cause deep, permanent scars.
Who Can Be Affected by Acne?
Acne is most commonly seen in teenagers due to hormonal changes during puberty. However, it can also affect people in middle age or later in life.
Causes of Acne
Now that you're familiar with what acne is, its types, and who it affects, let’s explore its main causes.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations are a common cause of acne, particularly during puberty. Known as hormonal acne, it may also occur in people with poor diets, during pregnancy, or shortly after childbirth.
Medication Use
Certain medications can trigger acne as a side effect. Some drugs contain ingredients that can negatively affect the skin. If you have a history of acne or notice skin changes after starting a medication, it’s important to consult a doctor to determine whether the acne is a side effect.
Stress
Stress is another factor that can lead to acne. It disrupts hormone balance and stimulates excess sebum production, which can clog pores and lead to breakouts.
Unhealthy Diet
Poor eating habits are also linked to skin problems. Consumption of dairy products and high-glycemic foods has been associated with acne. If dietary changes improve your skin, consult a specialist to help create a suitable meal plan that supports your skin health.
Improper Skincare
Using unsuitable skincare products can also contribute to acne. Some cosmetics contain harsh ingredients that increase oiliness and clog pores.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics may also play a role. If acne runs in your family, you're more likely to experience it at some point in your life.
Symptoms of Acne
Acne symptoms vary depending on the type, and may include:
Pimples filled with pus
Small red or purple bumps
Clogged pores with black or white tips (blackheads and whiteheads)
Painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the skin (cysts)
Treatment of Acne
Treating acne is often a long process that requires patience. Here are some of the main treatment options:
Use of Proper Skincare Products
Using the right skincare products is essential. Always consult a dermatologist before buying any products. They can assess your skin and recommend the best options. Choosing products without professional guidance may worsen your condition.
Medication
Medication can also help treat acne, but should never be taken without a doctor’s prescription. Some medications may have side effects that could aggravate the skin.
Dietary Changes
Healthy eating plays a vital role. If you're struggling with acne, consider adding foods such as carrots, cantaloupe, pumpkin, spinach, and sweet potatoes to your diet. Don’t forget to drink enough water — it helps detoxify the body and reduce acne symptoms.
Light Therapy
In recent years, various types of light therapy have been used to treat acne. This type of treatment should only be prescribed and monitored by a medical professional.
Prevention
Acne can significantly impact your daily life. To reduce the risk of developing it, consider these preventive tips:
Wash Your Face with Warm Water and a Suitable Cleanser Daily
Wash your face at least twice a day with warm (not hot) water and a cleanser recommended by a dermatologist. This helps remove dirt, excess oil, and dead skin cells, lowering the risk of clogged pores.
Avoid Touching Your Face with Dirty Hands
Your hands come into contact with many dirty surfaces throughout the day. If you touch your face without washing your hands, you risk spreading bacteria and irritating the skin. Carry a hand sanitizer with you if frequent hand washing isn’t possible.
Conclusion
Acne is an unpleasant skin condition that can affect anyone. It manifests in different ways and can be triggered by numerous factors. To reduce your risk, take daily care of your skin and act at the first signs of acne.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. For more helpful content, visit our health portal.