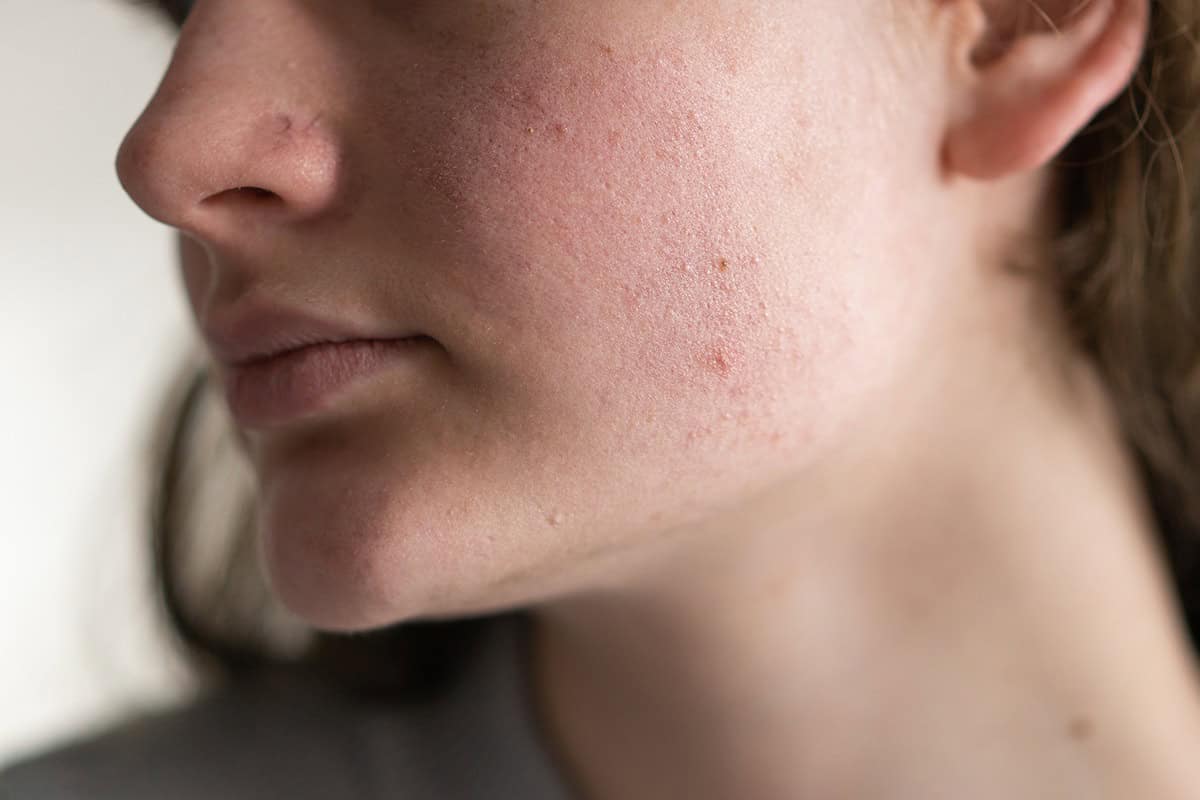
Rosacea is a common skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness and pimples. Although it usually doesn’t involve severe symptoms, it can significantly impact your self-esteem and quality of life.
If you want to learn more about rosacea, keep reading. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the condition, its causes, main symptoms, and the ways you can manage it.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic, non-contagious condition characterized mainly by facial redness. It typically affects the forehead, chin, cheeks, and the lower part of the nose. In rarer cases, it can also appear on the neck, back, and chest.
Aside from redness, small dilated blood vessels may become visible, along with acne-like cysts, often filled with pus.
Types of Rosacea
There are four types of rosacea, each with distinct symptoms. Keep in mind that more than one type can appear simultaneously. It’s important to take early action and see a dermatologist to prevent the condition from worsening.
Here’s a breakdown of the four types:
1. Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea
This is the most common form of rosacea. It is mainly characterized by facial redness and clearly visible blood vessels. Symptoms can flare up unexpectedly but often resolve quickly.
2. Papulopustular Rosacea
This type involves pus-filled or fluid-filled bumps, usually appearing on the cheeks, chin, and forehead. These bumps are often mistaken for acne.
3. Ocular Rosacea
As the name suggests, this type affects the eyes, causing irritation, redness, and persistent tearing. It can lead to light sensitivity and swollen eyelids, often presenting as painful styes.
4. Phymatous Rosacea (Rhinophyma)
The rarest form, it causes thickening and swelling of the nose, making the skin rough and uneven. It predominantly affects middle-aged and older men but can also appear in women.
Who is Most at Risk for Rosacea?
Rosacea can affect anyone, but it is more common in women, particularly those going through menopause, and individuals with fair skin. Symptoms typically begin after age 30, though children and teenagers can also develop it.
While women are more often affected, men tend to experience more severe symptoms—often due to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is still unknown. However, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
Genetics: A family history of rosacea increases your risk.
Environmental exposure: Frequent exposure to direct sunlight or strong winds can increase the likelihood of rosacea.
Other contributing factors include:
- Hot beverages
- Spicy foods
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Hot weather
- Emotional stress
I - ntense exercise, especially running
- Certain medications (e.g., those for high blood pressure)
- Hormonal imbalances
- Some skin and hair care products
- Symptoms of Rosacea
The most common symptom is facial redness, which can become chronic if ignored. This is particularly noticeable in people with fair skin.
Other possible symptoms include:
- Visible small blood vessels on the nose and cheeks
- Pus-filled pimples resembling acne, sometimes merging into larger inflamed areas
- Burning or stinging sensations on the skin
- Eye problems such as dryness, swelling, and irritation
- Thickened skin on the nose, making it appear larger and more sensitive
Additional symptoms may include:
- Sudden prickling or tingling sensations on the skin
- Enlarged pores
- Skin discoloration or patches
If you experience any of these, see a dermatologist promptly. Symptoms may go away temporarily but often return without proper treatment.
Treatment for Rosacea
There is currently no cure for rosacea, but the symptoms can be managed with the following methods:
1. Using Suitable Skincare Products
Over-the-counter skincare designed for rosacea can help, but consult a dermatologist before trying new products. Using the wrong product may worsen your symptoms.
2. Medication
Prescription medications can also be effective, but they should only be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser treatment is a modern method for reducing redness and inflammation. A dermatologist will determine if it's suitable for you and how often you’ll need sessions.
Prevention
While rosacea can't be entirely prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
Avoiding Triggers
Stay away from the known triggers: wind, heat, cold, stress, alcohol, smoking, and spicy foods.
Protecting Your Skin from the Sun
Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher all year round, regardless of the season. Sun exposure is a key aggravating factor for rosacea.
Following a Diet
Avoid or limit the following:
- Dairy products (except for cottage cheese)
- Soy sauce
- Chocolate
- Legumes
- Citrus fruits, tomatoes, bananas, figs, and raisins
- Eggplant, spinach, and avocado
- Spicy and hot foods
- Alcohol
- Daily Hydration
Proper skin hydration is essential. Avoid aggressive skincare ingredients and consult a dermatologist for suitable moisturizers and creams.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a skin condition that can affect your daily life. Although there's no cure, early action and proper management can help you maintain control and protect your quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you're interested in more health articles, feel free to explore our health portal.