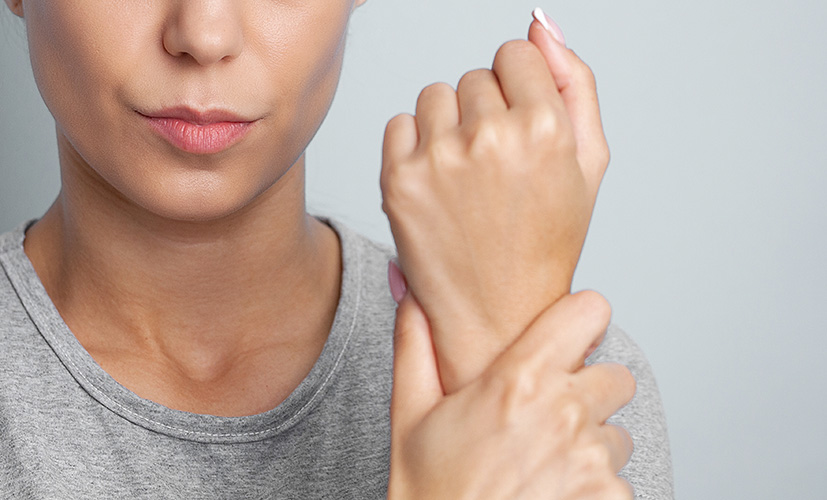
Arthritis is a common musculoskeletal disorder affecting millions of people worldwide. Depending on its severity, it can significantly restrict your movement and cause considerable discomfort, which may reduce your quality of life.
To learn more about this condition, read this article to the end. We will explore the most common types of arthritis in detail, highlight the main causes, mention some of the symptoms, and discuss treatment and prevention methods.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory joint condition characterized primarily by pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Depending on the type, it can develop gradually or suddenly, affecting both small and large joints.
Types of Arthritis
There are over 100 known types of arthritis, each with its own characteristics. Below, we discuss some of the most common forms.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, sometimes called arthritis of the hands, is a condition whose exact cause is still unknown. It begins in the synovial membrane of the movable joints, which is mistakenly attacked by the immune system because the body recognizes it as foreign. A key feature of this type is that it affects the same joints on both sides of the body. It mainly affects the hands and feet, but in severe cases can also involve wrists, shoulders, elbows, neck, etc. This condition is mostly found in women aged 40 to 60.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is caused by excessive strain on the joints. It is most common in people over 50, but can also affect younger individuals. Factors such as obesity or injuries can contribute to its development.
Osteoarthritis primarily affects weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips. The lubricating fluid that reduces friction in the joints decreases, causing severe pain.
Arthrosis
Arthrosis can affect one or more joints. It develops due to wear or damage of the cartilage and mostly occurs in people over 40. It is characterized by morning stiffness and pain that usually lasts about half an hour. These symptoms may also appear after prolonged sitting or extended movement.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the body mistakenly attacks healthy joints, causing inflammation. It is a long-term condition most commonly seen in people with psoriasis—a skin disorder characterized by red, painful, scaly plaques. It can affect small joints in the hands and feet, as well as larger ones like the knees and hips.
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis, also known as Reiter’s syndrome, is caused by an infection in the body. It can occur at any age.
This disease is characterized by swelling and pain, usually affecting the knees and ankles, and less commonly the hands. In some cases, it can also affect the eyes, skin, and urethra.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by elevated uric acid levels in the blood, often due to metabolic disturbances or unhealthy habits. This leads to the formation of crystals in joints, tendons, and tissues, causing inflammation. It typically starts with sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness around one or two joints, most commonly the big toe. Gout can also affect knees, elbows, and ankles, causing limited mobility and permanent joint damage. For more information, you can read our article dedicated to gout.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis, also known as Bechterew’s disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition primarily affecting the spine and hip joints. It mostly affects men aged 16 to 30 but can also develop in women.
Symptoms include limited spine mobility and pain after prolonged sitting or standing. Without early treatment, it can damage not only the spine but also the hips, shoulders, hands, and feet.
Other Types of Arthritis
As mentioned, arthritis includes over 100 types. Other forms include:
- Infectious arthritis — caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi entering the joints;
- Traumatic arthritis — resulting from injury or fracture;
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis — an autoimmune inflammation occurring in individuals under 16;
- Arthritis caused by connective tissue diseases — such as lupus or dermatomyositis;
- Rheumatism — a form of reactive arthritis developing after streptococcal infection;
- Viral arthritis — caused by viral infection.
- Risk Factors
Arthritis can affect anyone, regardless of gender or age. It is more common in people over 50 but can appear in younger individuals as well. Some risk factors include:
- Smoking — damages joints by reducing oxygen and nutrient supply;
- Obesity — increases joint strain, accelerating cartilage wear;
- Physical activity level — inactivity or excessive strain from sports can increase risk;
- Heredity — a family history of arthritis increases your risk;
- Other health conditions — autoimmune diseases affecting bones increase arthritis risk;
- Gender — women are more frequently affected.
- Causes of Arthritis
Common causes include:
- Aging — joints wear down over time;
- Weak immune system — low immunity can trigger arthritis;
- Viral infections — including COVID-19, can cause viral arthritis;
- Hormonal changes — fluctuations in hormone levels can contribute to arthritis.
Often, arthritis develops without a clear cause, making diagnosis and treatment more challenging.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Symptoms vary by type but often include:
- Joint pain;
- Redness;
- Discoloration around the joint;
- Stiffness or limited mobility;
- Swelling;
- Warmth in the affected area.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor promptly for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Methods
There is currently no cure for arthritis, but some treatments can alleviate discomfort, including:
- Anti-inflammatory medications;
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs);
- Physical therapy;
- Surgery.
Always consult a specialist before starting any treatment. Avoid self-medication as it may worsen your condition.
Prevention
Although some types of arthritis appear without a clear cause and cannot always be prevented, certain measures can help maintain joint health:
Avoid smoking;
Follow a healthy diet — consult a dietitian to create a personalized nutrition plan;
Exercise regularly — preferably with a specialist’s guidance who can recommend appropriate protective gear for joints during sports. If exercise is not possible, walking is a good alternative.
Conclusion
Arthritis is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders. It can affect people of all ages and cause significant discomfort. We hope this article has helped you better understand the most common types of arthritis and the prevention methods to protect your joints.
This article is for informational purposes and does not replace professional medical consultation. For more helpful articles, visit our health portal.