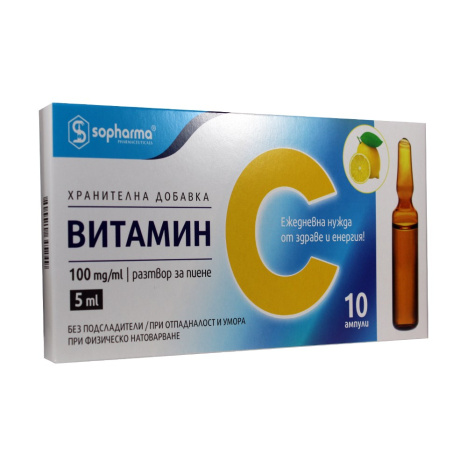
VITAMIN C 500mg/5ml for drinking x 10 amp Sopharma
Vitamin C drinking solution is used to stimulate the immune system and protect against viral and bacterial infections; It has an antioxidant and general strengthening effect; Strengthens vessels and reduces the risk of cardiovascular incidents; It favorably affects vision, skin, nails, muscles, joints and bones. It also helps to recover faster after illness, mental and physical strain. Available in a pack of 10 drinking ampoules.
It can also be used in the following cases:
• treatment of vitamin C deficiency in the body (scurvy); idiopathic methemoglobinemia;
• as additional therapy in conditions and diseases in which the need for ascorbic acid is increased: severe viral and bacterial infections; diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including during surgical interventions (prolonged diarrhea; peptic ulcers; gastrectomy, resection of the ileum); severe injuries, burns; neoplastic diseases; hemodialysis; hyperthyroidism; alcoholism.
Adults:
100 mg to 500 mg daily for at least 2 weeks. The maximum daily dose is 6 g.
Children:
100 mg to 300 mg daily for at least 2 weeks in divided doses.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction:
Acetylsalicylic acid:
With simultaneous administration with ascorbic acid, the excretion of the latter increases, and the release of salicylates slows down.
Warfarin:
When used in high doses, ascorbic acid can reduce the effect of oral anticoagulants.
Oral contraceptives:
Ascorbic acid in a dose of 1 g daily increases the bioavailability of ethinyl estradiol. This effect may be relevant if ascorbic acid therapy is discontinued. In this case, it is possible that the bioavailability of ethinyl-estradiol decreases, and this may increase the risk of unwanted pregnancy.
Products containing iron:
Ascorbic acid can increase the absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract.
Isoprenaline:
With simultaneous administration with ascorbic acid, the chronotropic effect of isoprenaline is reduced.
Flufenaziv, other phenothiazine derivatives:
The simultaneous use of ascorbic acid with phenothiazine derivatives leads to a decrease in their therapeutic effect.
Amphetamines and tricyclic antidepressants:
Ascorbic acid reduces the renal tubular reabsorption of amphetamines and tricyclic antidepressants.
Aminoglucoside antibiotics:
Aminoglucoside antibiotics are much more active against most microorganisms at pH 7-8, therefore ascorbic acid as an acidifying agent can reduce their effect at doses greater than 1 g.
Special warnings and precautions for use:
Ascorbic acid in high doses can cause an increase in the level of oxalates in the urine and promote the formation of kidney stones. Patients with impaired renal function or kidney stone disease may be more sensitive to this effect of the product. High doses of ascorbic acid (over 2 g daily) can cause hemolytic anemia in glucose-β-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Ascorbic acid should be used with caution in patients with hemochromatosis, thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, sideroblastic anemia.
Intravenous administration of ascorbic acid can be painful and less commonly cause thrombophlebitis, which is due to chemical irritation. Therefore, in diseases of the venous vascular system, thrombophlebitis and a tendency to thrombosis, intramuscular application of the product is preferable. Rapid intravenous injection of ascorbic acid should be avoided.
In high doses, ascorbic acid may compromise transaminase, lactate dehydrogenase, bilirubin, and fecal blood tests. Ascorbic acid as a redox compound affects various redox tests for determination of glucose in urine and serum. The administration of Vitamin C should be stopped 1-2 days before the test.
Sodium sulfite, which is part of the product, can rarely cause allergic reactions, including bronchospasm, especially in patients with a history of asthma or allergy.
Pregnancy:
For ascorbic acid, there are no clinical data on exposed pregnancies. Experimental studies in animals show no direct or indirect effects on pregnancy, embryonic/fetal development, parturition or 5.3). Prescribing ascorbic acid to pregnant women requires caution.
Breastfeeding:
Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk. When administered to lactating women according to dosage recommendations, it does not pose a risk to the infant.
Effects on the ability to drive and use machines:
Vitamin C Sopharma does not affect the ability to drive and operate machinery.
Special storage conditions:
Store in the original package in order to protect from light
To be stored below 25°C.
Do not freeze!
Keep out of the reach of children!
Adverse drug reactions:
Ascorbic acid in rare cases and when used in high doses can cause side effects:
Gastrointestinal disorders: nausea, vomiting, colic, diarrhea.
Kidney and urinary tract disorders: increased diuresis, nephrolithiasis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: redness of the skin.
Reactions at the site of administration: transient pain and edema with intramuscular administration.
Overdose:
Ascorbic acid is extremely well tolerated, even in high doses. No cases of acute overdose with severe consequences have been described. At very high doses - 5-10 g daily, it is possible to sometimes experience gastrointestinal disturbances, which are mainly due to the laxative effect of ascorbic acid.