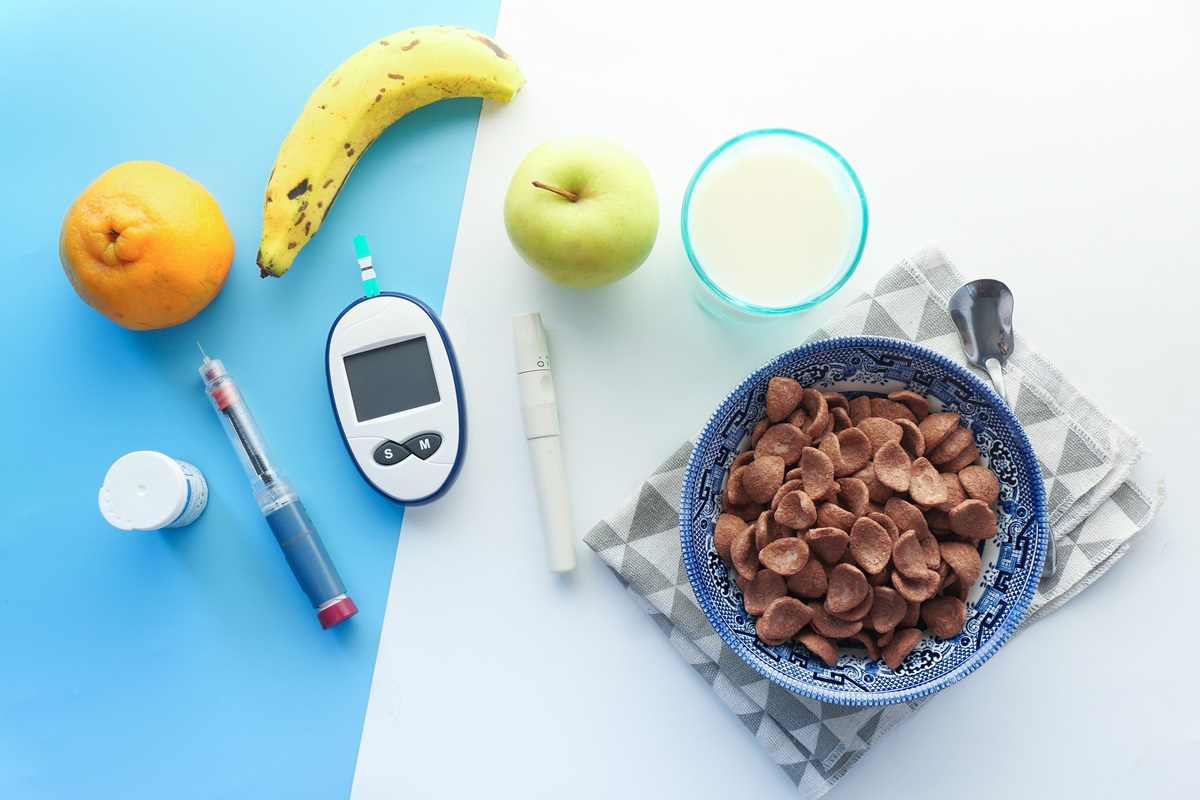
One of the most important indicators of overall health is blood sugar. Maintaining its normal levels is essential for the proper functioning of the body and for preventing possible health issues.
In this article, we will explore what blood sugar is, what its normal values are, how it is measured, and the consequences of having high or low blood sugar. We will also discuss useful practices to maintain optimal blood glucose levels.
What Is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is simply the main source of energy for the cells in our body. It mainly comes from the breakdown of carbohydrates in food. Once in the bloodstream, glucose is transported to all cells, providing them with the energy they need. Its role is vital for proper cell nourishment and overall body function.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
The importance of blood sugar is not only in its presence but mainly in its amount. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for health.
Blood glucose levels typically fluctuate throughout the day, depending on various factors like diet, physical activity, and others. That is why blood sugar is often measured fasting (in the morning before breakfast, coffee, etc.) or after eating to study the body's response to different foods and drinks.
Here is a table showing reference values for normal blood sugar, prediabetes, and diabetes:
- Test
- Normal
- Prediabetes
- Diabetes
- Fasting Blood Sugar
- 3.3 – 5.4 mmol/L
- 5.5 – 6.9 mmol/L
- Over 6.9 mmol/L
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- Under 7.8 mmol/L
- 7.8 – 11.1 mmol/L
- Over 11.1 mmol/L
- Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
- 4.0 – 5.6 %
- 5.7 – 6.4 %
- Over 6.4 %
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Normal fasting blood sugar values are usually between 3.9 and 5.5 mmol/L. Levels higher than 5.5 mmol/L may indicate prediabetes or diabetes.
Post-Meal Blood Sugar Levels
After eating, blood sugar levels rise but should not exceed 7.8 mmol/L two hours after a meal. Values above 7.8 mmol/L may signal problems with glucose metabolism or poor sugar processing.
Measuring Blood Sugar — Reference Values for Finger-Prick TestsOne of the most common and easy ways to measure blood sugar at home is using a glucometer. This involves pricking a finger to obtain a blood sample.
This method is fast and convenient, especially for people with diabetes who need to monitor their blood sugar regularly or to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Reference values for finger-prick tests are:
Fasting: 3.9 – 5.6 mmol/L
Two hours after eating: up to 7.8 mmol/L
Insulin and Its Role
Insulin is a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. It is produced and released by the pancreas as soon as blood sugar levels rise (especially after eating), helping cells absorb glucose to obtain the energy they need and maintain a healthy cycle.
However, if glucose absorption is poor and blood sugar levels remain too high or low, it affects insulin production and can lead to complex health problems.
Insulin Reference Values
Normal insulin levels vary based on individual characteristics such as gender, age, height, weight, and more. Below are approximate reference values for fasting insulin:
Age Group
Fasting Insulin (µIU/mL)
Children
2 – 19
Adults
2 – 25
High Blood Sugar: Causes, Symptoms, and Consequences
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when glucose levels in the blood are above normal.
Causes may include insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance.
If untreated, high blood sugar can cause serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
What Raises Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar levels can rise due to many factors, including stress, excessive consumption of sugary foods, or dehydration. If elevated levels persist, it indicates a more serious problem, such as the body not producing enough insulin.
Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
Common symptoms include dry mouth, constant thirst, and frequent urination. More severe symptoms may include chronic fatigue, headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, and nausea.
Consequences of High Blood Sugar
Chronic high blood sugar can lead to:
Insulin resistance: Reduced sensitivity to insulin, causing the pancreas to produce more insulin and potentially leading to diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis: Dangerous buildup of acids (ketones) in the body.
Cardiovascular diseases: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Nerve damage (neuropathy): High glucose can damage nerves, especially in the limbs.
Kidney problems: Potential kidney damage leading to chronic kidney failure.
Vision problems: Damage to the retina, possibly causing blindness.
Low Blood Sugar: Causes, Symptoms, and Consequences
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when blood glucose falls below normal levels.
This often happens due to overexertion, fasting, intense physical activity on an empty stomach, and more. It is advisable to always have something sweet on hand.
Neglecting low blood sugar can cause serious health problems or even be fatal, so it’s important to monitor your health and consult a doctor if you suspect issues.
Causes of Low Blood Sugar
Common causes include uncontrolled diabetes, prolonged fasting, alcohol or cigarette use on an empty stomach, certain medications, and kidney disease.
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, dizziness, numbness around the lips, trembling, blurred vision, excessive sweating, pale skin, and rapid heartbeat. Confusion or disorientation is also possible.
In severe cases, especially in diabetics, fainting, loss of consciousness, collapse, or more serious irreversible damage can occur.
- Possible Consequences of Untreated Low Blood Sugar
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Physical injuries from falls
Hypoglycemic coma, requiring emergency medical care
How to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Controlling blood sugar is key to preventing complications related to diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Here are some tips for maintaining healthy glucose levels:
Healthy Diet
- Limit sugary and simple carbohydrate-rich foods. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods help maintain healthy glucose levels.
- Regular Physical Activity
- Exercise supports healthy blood sugar regulation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Overweight is a major risk factor for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
- Especially important for people with diabetes or prediabetes to avoid complications. Home glucometers make this easy.
- Manage Stress
- Stress can raise blood sugar, so practices like meditation, yoga, or relaxation techniques are beneficial.
- Medication
If needed, a doctor may prescribe insulin or oral antidiabetic drugs based on individual needs.
Conclusion
Blood sugar is a key indicator of overall health. Keeping it within normal limits is crucial to preventing serious health problems.
Understanding normal blood sugar levels and the factors affecting them helps you take better care of yourself and your loved ones.
Regular monitoring, a healthy diet, physical activity, and stress management are essential habits for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
If you experience symptoms like fatigue, dry mouth, or unusual changes in your health, consult a healthcare professional promptly for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.