Redness of the Skin: Causes, Soothing Methods, and When to See a Dermatologist
Redness of the skin on the face and body is a common condition that can affect anyone. It is often accompanied by itching, pimples, or a burning sensation. This symptom may be caused by skin conditions, sun exposure, environmental triggers, allergies, stress, hormonal changes, or other internal and external factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common causes of skin redness, how to soothe irritated skin, and when it’s highly recommended to consult a dermatologist.
What Causes Skin Redness?
Skin redness can be temporary or persistent, localized or widespread, mild or severe. It occurs when the blood vessels in the skin dilate in response to irritation, inflammation, or other stimuli.
While any skin type can experience this issue, fair, thin, or sensitive skin is more prone to it due to a more fragile skin barrier.
Among the most common causes of facial redness are sunburn, allergic reactions, and even increased physical activity, such as a walk or a workout. Redness often resolves on its own, but if it worsens or is accompanied by symptoms like stinging, itching, or a rash, a consultation with a specialist is recommended.
Understanding the potential triggers—both external and internal—is key to proper treatment.
External Causes of Skin Redness
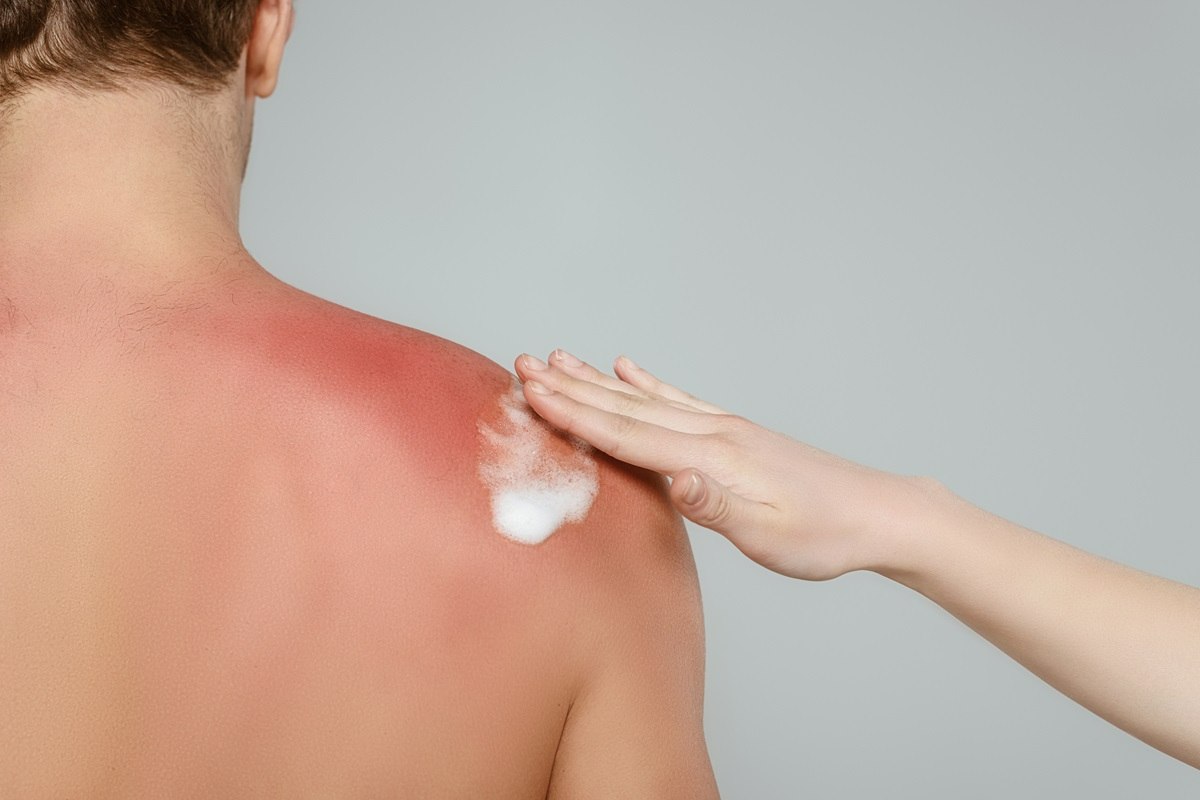
Sun exposure: One of the most common causes. Prolonged unprotected exposure to UV rays can lead to sunburn, redness, pain, swelling, or even blistering.
Environmental factors: Extreme temperatures, strong wind, and pollution can irritate the skin and cause vascular reactions.
Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, and dust mites may trigger an inflammatory response in sensitive skin.
Irritants: Harsh soaps, laundry detergents, and fragranced products often cause irritation and redness.
Insect bites or stings: These can lead to localized redness, swelling, and itching.
Friction: Tight clothing, shoes, or sports equipment may cause irritation and redness due to constant rubbing.
Heat and radiation: High temperatures or radiation (e.g., from certain medical treatments) may provoke skin inflammation.
Internal Causes of Skin Redness
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): An immune-mediated condition causing red, itchy, and inflamed skin.
Psoriasis: An autoimmune disorder that leads to red, scaly patches due to rapid skin cell turnover.
Food allergies: Trigger immune responses that may manifest as hives, redness, or swelling.
Drug reactions: Some medications may cause skin sensitivity or allergic reactions.
Hormonal changes:
Menopause: Often causes hot flashes and facial flushing.
Pregnancy: May increase blood flow to the skin, causing a rosy appearance or redness.
Stress and anxiety: Emotional triggers can cause facial flushing through the body's stress response.
Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections such as folliculitis or impetigo may also cause redness. Severe cases require medical treatment.
People with fair skin or a family history of skin conditions like rosacea or eczema are generally more susceptible to skin redness.
Redness Caused by Combined Factors: Rosacea
Some conditions, such as rosacea, are caused by both internal and external factors. Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that typically affects the face. It is characterized by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps.
Common triggers for rosacea include:
- Sun exposure
- Hot beverages
- Spicy foods
- Alcohol
- Stress
Managing rosacea requires ongoing care and lifestyle adjustments to prevent flare-ups and minimize persistent redness.How to Soothe
Red Skin
To effectively soothe red or irritated skin, it's important to identify and avoid the underlying cause—although this can be challenging without professional help. Treatment often includes:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Antihistamines
- Anti-itch creams
- Antibiotics or antibiotic creams
- Soothing skincare products recommended by a dermatologist
Prevention Tips
Preventing redness starts with protecting your skin from sun damage and avoiding known triggers. Here are key prevention strategies:
Always apply sunscreen and avoid extended sun exposure without protection.
Avoid irritants, such as:
- Extreme weather
- Smoking
- Allergens (pollen, dust mites)
- Triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, and excessive caffeine
- Avoid hot showers; opt for lukewarm water instead.
- Maintain a gentle skincare routine:
- Use hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and non-irritating products.
- Choose moisturizers designed for redness-prone or sensitive skin. These often include ingredients with a cooling and barrier-strengthening effect.
- Cleanse using mild, non-abrasive formulas and soft cotton pads—avoid rubbing or scrubbing.
Avoid makeup wipes, as they can be harsh and irritating.
Ingredients that help soothe irritated skin include:
- Cucumber extract
- Aloe vera
- Allantoin
- Green tea
- Niacinamide
If you wish to cover mild redness, tinted moisturizers are a great option. They provide light coverage, hydration, and are usually less likely to cause irritation compared to heavier makeup.
When to See a Dermatologist
In many cases, redness is temporary and harmless. But if it becomes frequent, persistent, or worsens over time, it's important to seek medical advice. It could be a sign of an underlying condition that requires professional treatment.
In Conclusion
Redness of the skin can result from a wide range of factors—environmental, internal, or both. By identifying the triggers and applying appropriate prevention and treatment strategies, you can manage symptoms effectively and reduce discomfort.
This includes:
- Seeing a dermatologist when necessary
- Avoiding skin irritants
- Using sunscreen daily
- Choosing the right skincare for your skin’s specific needs
- With the right approach, you can maintain a healthy, radiant complexion while minimizing the risk of recurring redness.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. For more health-related content, visit our health portal.