As we age, many of us look for ways to slow down the aging process. In recent years, resveratrol—a powerful antioxidant—has gained popularity in the anti-aging space for its promising effects. If you haven’t heard of it yet, read on. This article explains what resveratrol is, how it combats aging, its additional health benefits, and how to take it safely and effectively.
What is Resveratrol?
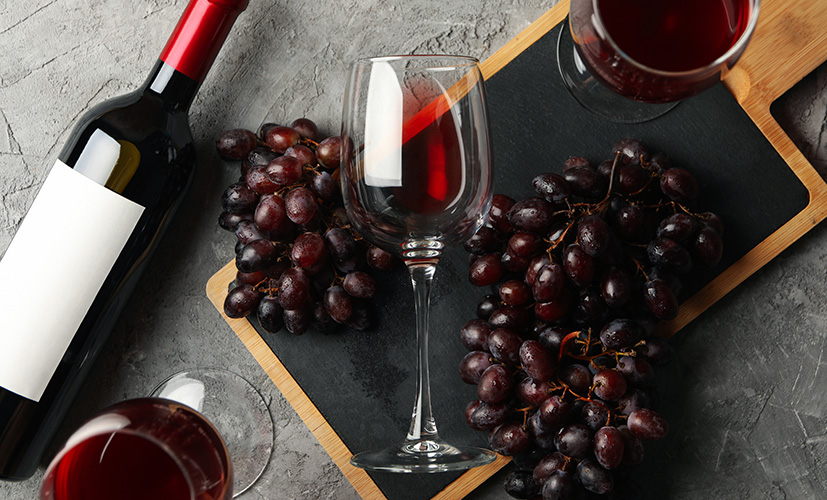
Resveratrol is a potent antioxidant naturally found in some fruits and plants, such as red grapes. It was first discovered in 1939 by a Japanese scientist who identified it in the roots of the white hellebore plant. At the time, it didn’t attract much scientific interest and wasn’t studied further.
That changed in the 1990s with the emergence of the so-called French paradox—the observation that people in France had relatively low rates of heart disease despite a diet high in saturated fats. Further investigation revealed that this phenomenon could be partially attributed to regular consumption of red wine, which contains resveratrol. Since then, resveratrol has been dubbed the “longevity molecule,” and scientists continue to study its full range of health benefits.
Main Sources of Resveratrol
As mentioned, red grapes are a key source of resveratrol. Other sources include:
- Peanuts
- Blueberries
- Cherry tomatoes
- Plums
- Raspberries
- Cocoa and dark chocolate
Resveratrol as an Anti-Aging Agent
Resveratrol has the potential to slow down the aging process, primarily by activating sirtuins—particularly SIRT1—known as the “longevity genes.” These proteins help regulate cellular aging and stress responses. When activated, they can delay cell senescence, improving overall cellular health.
As a powerful antioxidant, resveratrol also protects DNA from oxidative damage—a major contributor to aging. It neutralizes free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress at the cellular level. This supports optimal cell function, slows aging, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Additional Health Benefits of Resveratrol
Supports Brain and Heart Health
Resveratrol may support the health of the brain and cardiovascular system, helping reduce the risk of conditions like stroke and heart attack. It helps keep blood vessels flexible, prevents plaque buildup, and promotes proper circulation—ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach cells efficiently.
In the brain, resveratrol protects neurons from oxidative stress and preserves synaptic connections, reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and dementia. Improved cerebral blood flow also enhances memory and concentration.
Boosts Good Cholesterol
Regular intake of resveratrol, through diet or supplements, may increase HDL (“good” cholesterol) and lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol), reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and supporting better blood flow.
Helps Regulate Blood Sugar
Resveratrol can assist in controlling blood sugar levels—particularly beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes or genetic predisposition. It improves glucose uptake by cells and supports pancreatic function, enhancing insulin production.
Protects Liver Function
A healthy liver is crucial for detoxification. Resveratrol can help prevent fatty liver and fibrosis—a condition where excess connective tissue builds up. This is particularly important for people who consume alcohol, eat poorly, or take strong medications.
Helps Combat Acne
Due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, resveratrol can reduce inflammation in the skin and regulate sebum production—preventing clogged pores and breakouts.
Protects Skin from UV Radiation
Frequent sun exposure accelerates skin aging and can lead to skin cancer. Resveratrol acts as a protective shield against harmful UV rays. However, it should be used in combination with a high-SPF sunscreen and sun-avoidance during peak hours.
Improves Eye Health
Resveratrol protects the eyes from damage caused by free radicals and may help prevent conditions like cataracts. It can also reduce eye fatigue and support better vision.
Supports Joint Health
Joints are prone to wear and tear, especially in older adults and active individuals. Resveratrol may help by stimulating collagen production, which maintains joint flexibility and reduces cartilage degradation.
May Help in Cancer Prevention
Resveratrol is under active investigation for its potential anti-cancer effects. Some studies suggest it can inhibit cancer cell growth by disrupting the cell cycle and preventing DNA mutations caused by free radicals. It has shown the most promise in the prevention of breast, skin, prostate, and colon cancers.
How to Take Resveratrol
The ideal dosage of resveratrol depends on factors such as age, sex, and health status. Typically, the recommended daily dose ranges between 100 and 500 mg, but individual needs vary.
If you prefer getting resveratrol from food, consult a registered dietitian to develop a balanced meal plan that includes sufficient amounts of the antioxidant.
If you opt for a dietary supplement, it's important to first speak with a healthcare provider. They may run blood tests to recommend the most suitable product and dosage. Avoid self-prescribing resveratrol supplements, as misuse can lead to side effects like:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Liver dysfunction
Conclusion
Resveratrol is a well-studied antioxidant with significant promise in combating aging and improving overall health. To maximize its benefits, consult a healthcare professional to determine the best form and dose for your specific needs.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. For more health-related content, explore our health portal.