ZETHRUM powder for susp. 100mg/5ml 20ml
Leaflet: information for the user
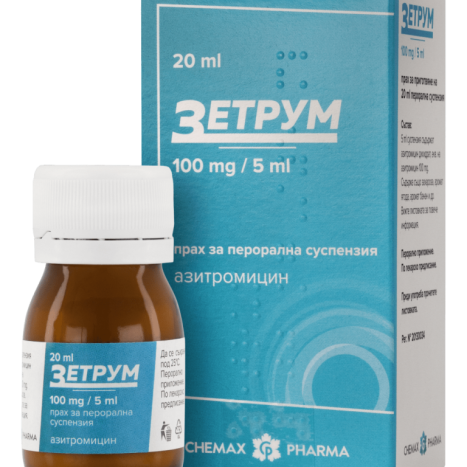
ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension
ZETHRUM 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension
azithromycin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you personally. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What this leaflet contains
1. What ZETRUM is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take ZETRUM
3. How to take ZETRUM
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store ZETRUM
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What ZETRUM is and what it is used for
ZETRUM contains the active substance azithromycin. Azithromycin is an antibiotic that belongs to a group of antibiotics known as macrolides, which block the growth of sensitive bacteria.
ZETRUM is used to treat the following infections:
Children aged 6 months and older weighing less than 45 kg
- Infections of the tonsils (tonsillitis) or throat (pharyngitis) caused by streptococcal bacteria
- Bacterial sinus infections (sinusitis)
- Bacterial infections of the middle ear (otitis media)
- Pneumonia (community-acquired, non-hospital-acquired pneumonia)
- Bacterial infections of the skin and underlying tissues
- Localized early stage Lyme disease (erythema migrans, caused mainly by tick bites)
- Bacterial infections of the gums (periodontitis) or gum abscess (periodontal abscess)
Adults and adolescents weighing at least 45 kg and with difficulty swallowing:
In addition to the infections listed above, ZETRUM can also be taken to treat the following infections:
- Infections of the urinary tract and cervix caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis
- Infections of the urinary tract and cervix caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae. ZETRUM should be used in combination with another antibiotic chosen by your doctor or pharmacist.
- Chronic inflammation of the prostate gland caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis
- Bacterial infections of the genitals with painful ulcers (chancre)
- Infections caused by a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) in people with advanced HIV infection. Zetrum should be used in combination with another antibiotic called ethambutol.
- Adults with chronic inflammation of the lungs (chronic bronchitis) or with bacterial infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries (pelvic inflammatory disease), in the latter always in combination with other antibiotic(s) chosen by your doctor.
ZETRUM is also taken to prevent infections caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) in people living with HIV infection.
2. What you need to know before you take ZETRUM
Do not take ZETRUM
- if you are allergic to azithromycin, erythromycin or any other macrolide antibiotic, or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking ZETRUM if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
• heart problems (e.g. heart rhythm problems or heart failure) or low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood: these conditions may contribute to serious cardiac side effects of azithromycin;
• liver problems: your doctor may need to monitor your liver function or stop treatment;
• severe diarrhea after taking other antibiotics;
• localized muscle weakness (in myasthenia gravis), as the symptoms of this disease may worsen during treatment;
• or if you are taking ergot alkaloid derivatives, such as ergotamine (used to treat migraine), as these medicines should not be taken together with ZETRUM.
Stop taking this medicine and contact your doctor immediately (see also “Serious side effects” in section 4):
• if you feel you are having an allergic reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rash, blistering);
• if you notice any symptoms as described in section 4 related to serious skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which have been reported in association with azithromycin treatment;
• if you feel that you have an altered heart rhythm or palpitations, feel dizzy or faint when taking ZETRUM;
• if you develop signs of liver problems (e.g. dark urine, loss of appetite or yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes);
• if you develop severe diarrhoea during or after treatment. Do not take any medicine to treat diarrhoea without first consulting your doctor. If diarrhoea persists or recurs within the first weeks after treatment, please also inform your doctor.
Superinfection
Your doctor may monitor you for signs of additional bacterial or fungal infections that cannot be treated with ZETRUM (superinfection).
Sexually transmitted infections
Your doctor may test you for a possible infection - syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease, to rule it out, because otherwise it can progress undetected and its diagnosis may be delayed. In addition, in any case of bacterial sexually transmitted infections, your doctor will start follow-up laboratory tests to monitor whether therapy is successful.
Children and adolescents
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if your child is under 6 months of age, as the efficacy and safety of this medicine have not been established in such children.
This medicinal product is not recommended:
if you are under 18 years of age and have been diagnosed with pelvic inflammatory disease
· under 12 years of age and at risk of infection with microorganisms belonging to the Mycobacterium avium complex, which usually affects people living with HIV who have weak immune systems, as its efficacy and safety have not been studied in these cases.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants
If your child is under 6 months old and your doctor has recommended treatment with azithromycin, stop giving him this medicine and contact your doctor immediately if he has significant vomiting or becomes irritable during or shortly after feeding.
Other medicines and ZETRUM
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Taking ZETRUM at the same time as some other medicines may cause side effects. Therefore, it is especially important to tell your doctor if you are using any of the following medicines:
• atorvastatin and other statin drugs (to reduce blood cholesterol and prevent heart disease, including heart attack and stroke);
• ciclosporin (to prevent the body from rejecting transplanted organs);
• colchicine (for the treatment of gout and familial Mediterranean fever);
• dabigatran (for the prevention and treatment of blood clots (anticoagulant));
• digoxin (for the treatment of heart disease);
• warfarin or similar medicines used to thin the blood (anticoagulants);
• medicines that may cause the heart muscle to contract and relax more slowly than normal (QT prolongation), such as the following:
- quinidine, procainamide, dofetilide, amiodarone and sotalol (to treat irregular heartbeat, including a heartbeat that is too fast or too slow - cardiac arrhythmia);
- pimozide (to treat mental illness);
- citalopram (for the treatment of depression);
- mofloxacin and levofloxacin (antibiotics);
- cisapride (for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases);
- hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine (to treat autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, or to treat or prevent malaria).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to become pregnant, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Your doctor will decide whether you should take this medicine during pregnancy only after making sure that the benefits outweigh the possible risks.
Breastfeeding
ZETRUM passes into breast milk. Therefore, your doctor will decide whether you should stop breast-feeding or whether you should refrain from treatment with ZETRUM, taking into account both the benefit of breast-feeding for your child and the benefit of therapy for you.
Driving and using machines
ZETRUM has a moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines. ZETRUM has been reported to cause dizziness, drowsiness and seizures, as well as vision and hearing problems in some people. These possible side effects may affect your ability to drive and use machines.
ZETRUM contains sucrose
ZETRUM contains sucrose as an excipient, which should be taken into account when treating patients with diabetes mellitus.
1 bottle of ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension 20 ml contains 14.484 g of sucrose. Each 5 ml of the prepared suspension contains 3.621 g of sucrose.
3. How to take ZETRUM
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
The recommended doses and duration of treatment are as follows:
Children aged 6 months and older weighing less than 45 kg
Infection
Azithromycin treatment course
Bacterial sinus infections (sinusitis)
Pneumonia (community-acquired, non-hospital-acquired pneumonia)
Bacterial infections of the skin and underlying tissues
Bacterial infections of the gums (periodontitis) or gum abscess (periodontal abscess)
There is a 3-day or 5-day course of treatment for these infections
3-day course of treatment
10 mg/kg/day for 3 days
5-day course of treatment
10 mg/kg taken on the first day of treatment, then 5 mg/kg taken once daily for the next 4 days
Bacterial infections of the middle ear (otitis media)
There is a 1-day, 3-day, or 5-day course of treatment for this infection.
1-day course of treatment
single dose 30 mg/kg
3-day course of treatment
10 mg/kg/day for 3 days
5-day course of treatment
10 mg/kg taken on the first day of treatment, then 5 mg/kg taken once daily for the next 4 days
Infections of the tonsils (tonsillitis) or throat (pharyngitis) caused by streptococcal bacteria
There is a 3-day or 5-day course of treatment for these infections
3-day course of treatment
20 mg/kg/day for 3 days
5-day course of treatment
12 mg/kg/day for 5 days
Localized early stage Lyme disease (erythema migrans, caused mainly by tick bites)
20 mg/kg taken on the first day of treatment, then 10 mg/kg taken once daily for the next 9 days
It is important to make sure that you use the amount of ZETRUM indicated in the table below according to the patient's body weight, the infection being treated and the specific course of treatment (1-day, 3-day, 5-day, 10-day) that you should follow, as instructed by your doctor or pharmacist.
Body weight (kg)
Maximum daily dose of azithromycin
5 mg/kg
10 mg/kg
12 mg/kg
20 mg/kg
30 mg/kg
7
2.00 ml (40 mg)+
3.50 ml (70 mg)
4.50 ml (90 mg)++
7.00 ml (140 mg)*
10.50 ml (210 mg)*
8
2.00 ml (40 mg)
4.00 ml (80 mg)
5.00 ml (100 mg)++
8.00 ml (160 mg)*
12.00 ml (240 mg)*
9
2.50 ml (50 mg)+
4.50 ml (90 mg)
5.50 ml (110 mg)++*
9.00 ml (180 mg)*
13.50 ml (270 mg)*
10
2.50 ml (50 mg)
5.00 ml (100 mg)
6.00 ml (120 mg)*
10.00 ml (200 mg)*
15.0 ml (300 mg)*
11
3.00 ml (60 mg)+
5.50 ml (110 mg)*
6.50 ml (130 mg)++*
11.00 ml (220 mg)*
16.50 ml (330 mg)*
12
3.00 ml (60 mg)
6.00 ml (120 mg)*
7.50 ml (150 mg)++*
12.00 ml (240 mg)*
18.00 ml (360 mg)*
13
3.50 ml (70 mg)+
6.50 ml (130 mg)*
8.00 ml (160 mg)++*
13.00 ml (260 mg)*
19.50 ml (390 mg)*
14
3.50 ml (70 mg)
7.00 ml (140 mg)*
8.50 ml (170 mg)++*
14.00 ml (280 mg)*
21.00 ml (420 mg)*
15
4.00 ml (80 mg)+
7.50 ml (150 mg)*
9.00 ml (180 mg)*
15.00 ml (300 mg)*
22.50 ml (450 mg)*
16‑25
5.00 ml (100 mg)
10.00 ml (200 mg)*
12.50 ml (250 mg)*
20.00 ml (400 mg)*
30.00 ml (600 mg)*
26‑35
7.50 ml (150 mg)*
15.00 ml (300 mg)*
17.50 ml (350 mg)*
25.00 ml (500 mg) *#
45.00 ml (900 mg)*
36- < 45
10.00 ml (200 mg)*
20.00 ml (400 mg)*
22.50 ml (450 mg)*
25.00 ml (500 mg) *#
60.00 ml (1,200 mg)*
^after preparation the concentration of the oral suspension is 20 mg/ml and the total volume of the suspension in the bottle is 20 ml.
+ The doses are rounded to obtain the appropriate dose to be administered if a graduated oral syringe with 0.5 ml graduations is used. Exact doses can be administered with a graduated oral syringe with 0.25 ml graduations.
++ Doses are rounded to obtain the appropriate dose to be administered if a graduated oral syringe with 0.5 ml graduations is used. Exact doses can be administered with a graduated oral syringe with 0.2 ml graduations.
* azithromycin 40 mg/ml (200 mg/5 ml) powder for oral suspension is most suitable for use in such patients.
# Do not exceed the daily dose for adults of 500 mg.
Adult and adolescent patients weighing at least 45 kg and with difficulty swallowing
Infection
Azithromycin treatment course
Infections of the tonsils (tonsillitis) or throat (pharyngitis) caused by streptococcal bacteria
Bacterial sinus infections (sinusitis)
Bacterial infections of the middle ear (otitis media)
Bacterial infections in patients with chronic inflammation of the lungs (chronic bronchitis)*
Pneumonia (community-acquired, non-hospital-acquired pneumonia)#
Bacterial infections of the skin and underlying tissues
Bacterial infections of the gums (periodontitis) or gum abscess (periodontal abscess)
There is a 3-day or 5-day course of treatment for these infections and the amount of ZETRUM to be taken each day is described for these courses of treatment below.
3-day course of treatment
25 ml (500 mg) taken once daily for 3 days
5-day course of treatment
25 ml (500 mg) taken on the first day of treatment, then 12.5 ml (250 mg) taken once daily for the next 4 days
Localized early stage Lyme disease (erythema migrans, caused mainly by tick bites)
50 ml (1,000 mg) taken on the first day of treatment, then 25 ml (500 mg) taken once daily for the next 9 days
Urinary tract and cervical infections caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis
50 ml (1,000 mg) taken as a single dose
Infections of the urinary tract and cervix caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae. ZETRUM should be used in combination with another antibiotic chosen by your doctor or pharmacist.
50 ml (1,000 mg) or 100 ml* (2,000 mg) as a single dose
Chronic inflammation of the prostate gland caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis
25 ml/day (500 mg) on 3 consecutive days per week, for 3 weeks
Bacterial infections of the genitals with painful ulcers (chancre)
50 ml (1,000 mg) taken as a single dose
Infections caused by a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) in people with advanced HIV infection. Zetrum should be used in combination with another antibiotic called ethambutol.
30 ml (600 mg) once a day
Preventing infections caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) in people living with HIV infection
60 ml (1,200 mg) once a week
Bacterial infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries (pelvic inflammatory disease) - in combination with other antibiotic(s) chosen by your doctor or pharmacist*
Only if treatment was started with azithromycin administered intravenously:
12.5 ml (250 mg) once daily to complete a 7-day course of treatment
* only in adult patients
# in adult patients oral treatment may follow initial intravenous treatment
Use in children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of azithromycin have not been established in children under 6 months of age for any of the indications listed in section 1.
Method of administration
For oral use after reconstitution.
The dose should be determined as accurately as possible using the 5 ml oral dosing syringe provided in the package. The syringe is graduated in 0.5 ml increments, providing 10 mg of azithromycin per division.
ZETRUM should be administered orally as a single daily dose. The oral suspension may be taken with or without food. Taking this medicine just before a meal may help to relieve stomach upset.
If the bottle of ZETRUM that you received from your doctor or pharmacist contains only powder, without liquid, then you must add a specific volume of water to the bottle before it is ready for use.
Method of preparation of the suspension
1. The bottle contains a powder from which an oral suspension is prepared by adding water.
2. Open the bottle.
3. Add 12 ml of water to the bottle using the oral syringe (supplied in the box).
4. Shake the bottle well until a uniform suspension is obtained.
5. The suspension thus prepared can be used for 5 days.
6. Shake the suspension before each use.
Instructions for using the dosing syringe
1. Dip the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the suspension and use the plunger to withdraw the required amount.
2. Place the child in a feeding position, place the tip of the syringe in their mouth and slowly inject the suspension.
3. After taking the medicinal product, give the child a small amount of juice or water.
4. After use, rinse the syringe with water and dry.
5. Store the oral dosing syringe in a dry and clean place.
If the powder has already been dissolved for you by your doctor or pharmacist, you can skip directly to the section “Instructions for taking each daily dose of ZETRUM oral suspension” below.
If you take more ZETRUM than you should
If you take more ZETRUM than you should, you may feel unwell. Typical signs of overdose are vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain and nausea. You should tell your doctor immediately or contact the emergency department of your nearest hospital.
If you forget to take ZETRUM
If you forget to take ZETRUM, take it as soon as possible, provided that it is at least 12 hours before the time for your next dose. If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the usual time. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you stop taking ZETRUM
If you stop taking ZETRUM too early, the infection may come back. Take ZETRUM for the full course of treatment, even when you start to feel better.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
Stop using ZETRUM and seek medical help immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
• sudden wheezing, difficulty breathing, swelling of the eyelids, face or lips, rash or itching, especially if affecting the whole body (anaphylactic reaction with unknown frequency);
• fast and irregular heartbeat (cardiac arrhythmia or torsades de pointes tachycardia, frequency unknown);
• dark urine, loss of appetite or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, which may be signs of liver disease (liver failure or hepatic necrosis (frequency not known), hepatitis (uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people)).
• severe diarrhoea with abdominal cramps, bloody stools and/or fever may mean that you have an infection of the colon (antibiotic-associated colitis, frequency unknown). Do not take antidiarrhoeal medicines that slow down bowel movements (medicines that inhibit peristalsis).
• reddish, flat, target-like or circular spots on the body, often with blisters in the centre, peeling skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals and eyes. These serious skin rashes may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome# or toxic epidermal necrolysis, frequency unknown).
• widespread rash, high body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes (DRESS syndrome or drug hypersensitivity syndrome, rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people));
• a red, scaly, widespread rash with lumps under the skin and blisters, accompanied by fever. Symptoms usually appear when treatment is started (acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis, rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)).
Other side effects
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- diarrhea
- abdominal discomfort*
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- headache
- vomiting, stomach pain#, nausea#
- Abnormal blood test results (decreased lymphocyte count, increased eosinophil count, increased basophil count, increased monocyte count, increased neutrophil count, decreased blood bicarbonate level)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- thrush (candidiasis) - fungal infection of the mouth and vagina, other fungal infections
- pneumonia, bacterial infection of the throat, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory disorder, inflammation of the mucous membrane in the nose, vaginal infection;
- changes in the number of white blood cells (leukopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia);
- increased platelet count;
- decrease in the ratio of blood cell volume to total blood volume (decreased hematocrit);
- allergic reactions, swelling of the hands, feet and face (angioedema);
- lack of appetite#;
- nervousness, insomnia;
- dizziness, drowsiness (somnolence), change in taste sensation (dysgeusia)#, tingling or numbness (paraesthesia);
- impaired vision#;
- ear disorder;
- feeling of spinning (vertigo);
- heart palpitations;
- hot flashes;
- sudden onset of wheezing, nosebleeds;
- constipation, flatulence, indigestion (dyspepsia), inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), bloating, dry mouth, belching (eructation), mouth ulcers, increased salivation;
- rash#, itching#, hives (urticaria)#, dermatitis, dry skin, excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- swelling and pain in the joints (osteoarthritis), muscle pain, back pain, neck pain;
- painful urination (dysuria), kidney pain;
- uterine bleeding outside the menstrual cycle (metrorrhagia), testicular disorder;
- swelling due to fluid retention, especially in the face, ankles and feet (edema, facial swelling, peripheral edema)
- weakness, fatigue, general feeling of malaise, fever;
- chest pain, pain;
- abnormalities in laboratory test results (e.g. blood and liver tests);
- a complication that occurred after an intervention.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- irritability;
- liver problems, yellowing of the skin or eyes;
- increased sensitivity to light#.
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- reduced number of red blood cells due to increased cell breakdown, which can cause fatigue and pale skin (haemolytic anaemia);
- reduction in the number of platelets in the blood, which can lead to bleeding and bruising (thrombocytopenia);
- anger, aggressiveness, feeling of fear and restlessness (anxiety), acute state of confusion (delirium);
- hallucination;
- fainting (syncope);
- seizures (convulsions);
- reduced sensation of touch, pain and temperature (hypoesthesia)#;
- feeling of hyperactivity;
- change in sense of smell (anosmia, parosmia);
- complete loss of taste (ageusia);
- muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis);
- abnormalities in the recording of the electrical activity of the heart on the electrocardiogram (ECG) (prolongation of the QT interval);
- deafness#, reduced hearing# or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)#;
- low blood pressure;
- inflammation of the pancreas causing very severe pain in the abdomen and back (pancreatitis);
- change in tongue color;
- joint pain (arthralgia)#;
- inflammation of the kidneys (interstitial nephritis) and kidney failure.
* These adverse reactions have only been observed with the use of azithromycin for the prevention and/or treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex infections in people living with HIV with insufficient recovery of the immune system.
# These side effects are more common when azithromycin is used for the prevention and/or treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex infections in people living with HIV with insufficient immune system recovery.
Reporting side effects
If you get any side effects, please tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly by:
Executive Agency for Medicines
8 Damyan Gruev Street
1303 Sofia
tel.: +359 2 8903417
website: www.bda.bg
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information about the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store ZETRUM
Store below 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and label after the abbreviation «EXP». The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
The ready-to-use oral suspension can be used within 5 days.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines you no longer use. This will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension contains
- The active substance in 5 ml of suspension is azithromycin dihydrate, equivalent to azithromycin 100 mg.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: sucrose, mannitol, sodium carbonate, xanthan gum; colloidal anhydrous silica, strawberry flavor, banana flavor, saccharin sodium.
What ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml powder for oral suspension looks like and contents of the pack
ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml, 20 ml powder for oral suspension is a white to off-white powder mixture, which is mixed with water to obtain a white to off-white homogeneous suspension with a strawberry aroma and a slight banana odor.
ZETRUM 100 mg/5 ml, 20 ml powder for oral suspension is packed in a 30 ml brown glass bottle with a polyethylene screw cap, with a protective ring. 1 bottle, together with a patient leaflet and an oral dosing syringe, are placed in a single folding carton.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Himax Pharma Ltd.
8A Goritsa Street
1618 Sofia, Bulgaria
tel. 02 955 6298
e-mail: office@chemaxpharma.com
This leaflet was last revised in: October 2025.