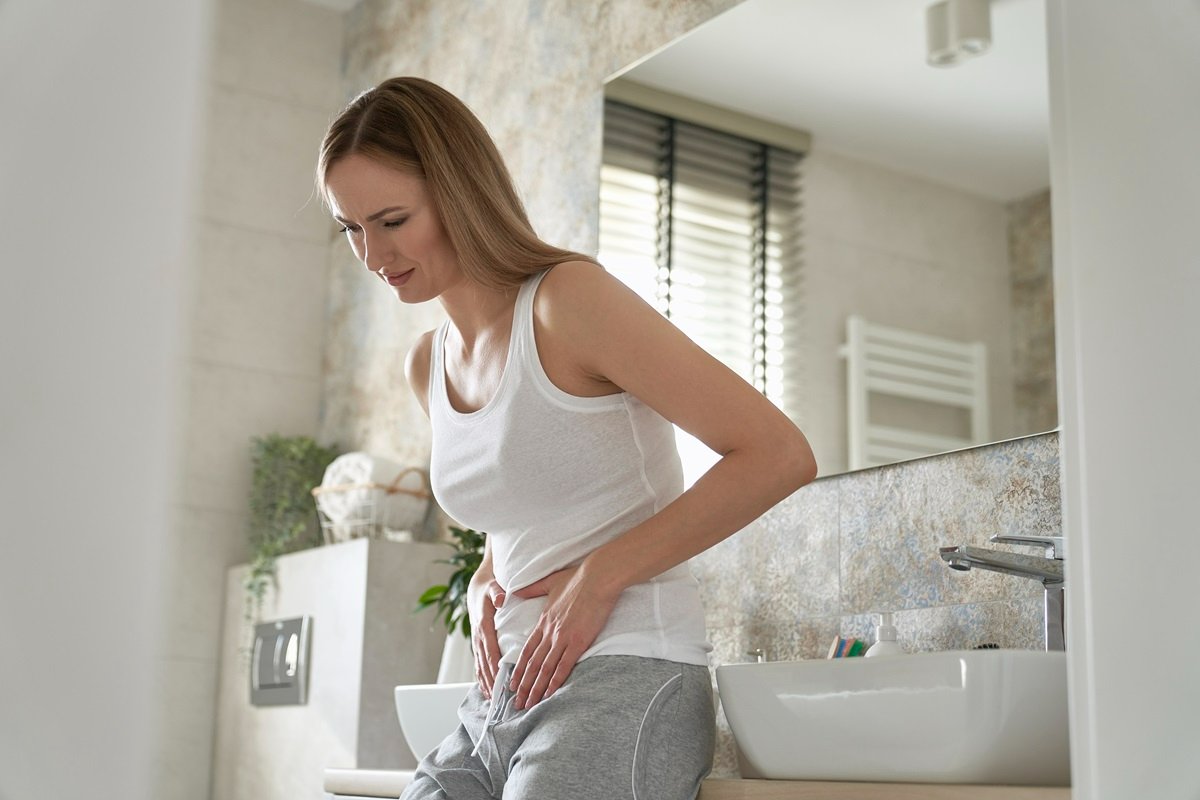
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, most often caused by an infection. Although the condition mainly occurs in women, it is possible for men to develop cystitis as well.
Many factors influence the occurrence of cystitis. Some of them include urinary retention, fatigue, constipation, pregnancy, as well as conditions caused by other diseases. The condition can cause discomfort, burning, and pain when urinating, as well as fatigue.
In this article, we will look at the causes of cystitis, its symptoms, and how to manage it.
Types of Cystitis
There are several types of cystitis. Here, we will explain their characteristics in more detail.
Acute Cystitis
Acute cystitis is most often caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli. This microorganism is found in the digestive tract as well as other systems in the body. Its entry into the urinary system leads to frequent urges to urinate, burning, and pain, and in some cases, more severe symptoms.
Cystitis can also occur due to viral or fungal infections. If left untreated or improperly managed, it can become chronic.
Chronic Cystitis
Chronic cystitis is most often caused by a previous urinary tract infection that was not completely cured. In such cases, the symptoms may subside, but the infection remains in the body and can return at any time. Chronic cystitis can occur if immunity decreases or after experiencing stress, for example.
Non-Infectious Cystitis
Non-infectious cystitis occurs when there is a change in the chemical and biological balance of the body. Possible causes include trauma, medication, and other factors.
Radiation Cystitis
Radiation cystitis is a type of non-infectious cystitis. It occurs due to radiation exposure, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Causes of Cystitis
The causes of cystitis can vary. Below, we will examine some of them in more detail.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections usually occur when bacteria from the skin or intestines reach the bladder through the urethra. This is one reason why cystitis is less common in men. In males, the anus is farther from the urethra, making it more difficult for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Inability to Empty the Bladder
Difficulty emptying the bladder when urinating can lead to cystitis. This happens because bacteria are not fully flushed out of the urinary system with the urine, allowing them to remain and multiply.
Some possible obstacles that prevent complete bladder emptying include:
- Presence of a bladder stone blocking the urinary system
- Pregnancy
- Infection
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Enlarged prostate gland in men
- Diabetes
People with diabetes are more prone to cystitis due to higher sugar levels in the urine, which create an ideal environment for bacterial growth. If bacteria enter the bladder, they can potentially cause cystitis.
Menopause
In some cases of menopause, the lining of the urethra shrinks due to a lack of estrogen. This can negatively affect the body and allow bacteria in the vagina to multiply. From there, the urethra can become infected, and the infection can spread to the bladder.
Other Causes
Additional factors that may contribute to cystitis include:
- A weak immune system
- Chemical irritants (such as certain soaps)
- Bladder damage following surgery
- Long-term use of a catheter
- Symptoms of Cystitis
- Symptoms of cystitis can vary. In milder cases, symptoms usually resolve on their own within a few days. However, some cases require treatment, which may take longer.
The most common symptoms of cystitis include:
- Pain and/or burning when urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Dark or cloudy urine
- Strong, unpleasant urine odor
Cystitis also occurs in young children. They may exhibit some of the symptoms mentioned above, as well as others, such as:
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Lack of appetite
- Low energy levels
- Diagnosing cystitis in young children is more challenging because they may struggle to describe their symptoms accurately.
Possible Complications
If not properly treated, cystitis can lead to complications. Below, we will discuss some of the most common ones.
Kidney Infection
An untreated infection can spread to the kidneys, potentially causing permanent damage and impairing kidney function.
Blood in the Urine
In some cases, cystitis can lead to the presence of blood in the urine. Normally, blood cells are only visible under a microscope. If this occurs, proper treatment can usually resolve the issue. However, in some cases, blood may still be present even after treatment, necessitating further medical evaluation.
Sometimes, blood in the urine is visible to the naked eye. If this happens, it is important to see a doctor immediately to determine the cause.
How to Prevent Recurring Cystitis:
- Do Not Delay Urination
Ignoring the urge to urinate can negatively affect the body and increase the risk of cystitis. Make sure to empty your bladder regularly. - Avoid Using a Bathtub
People prone to infections are advised to avoid taking baths. Instead, showers are recommended to reduce the risk of cystitis. - Maintain Good Personal Hygiene
Proper hygiene is key to maintaining good health. Wash the genital area daily using suitable products to prevent irritation and infection. - Treatment of Cystitis
Treatment for cystitis depends on the severity of the symptoms. Regardless of whether they are mild or severe, seeking medical advice is recommended. - Home Treatment
Cystitis is often treated at home. Before seeing a doctor, you can take steps to ease discomfort, such as: - Drinking more fluids
Urinating whenever you feel the need
Applying a warm water bottle to your lower abdomen or between your thighs
Avoiding sexual activity
For severe pain, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or paracetamol can help reduce discomfort and inflammation. It is advisable to consult a doctor or pharmacist for the appropriate medication. - Antibiotic Treatment
Some cases of cystitis require antibiotics. Depending on the severity of the infection, treatment can last from a few days to up to 10 days.
Only a healthcare professional should prescribe antibiotics after conducting the necessary tests. Self-medicating with antibiotics can worsen the condition.
Antibiotics usually work quickly, but if there is no improvement, consult your doctor. Be aware that some antibiotics can have side effects, such as:
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Itching
- Rash
If you experience any of these side effects, stop taking the medication and consult your doctor.
Many people worldwide have experienced cystitis at least once in their lives. This condition can be highly uncomfortable, interfering with daily life.
Pain and burning when urinating, along with frequent urges to use the toilet, are symptoms that should not be ignored. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and restore your well-being.