Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a key role in heart, brain, and immune system health. They support cognitive function, reduce inflammation, and improve lipid profiles. In this article, we’ll explore how Omega-3s work, what benefits they offer, and why they are so important for the body.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids belong to the group of polyunsaturated fats – a type of fat that contains more than one double bond in its molecular structure. Our bodies cannot synthesize them on their own, so it’s important to obtain them through food or dietary supplements. These fatty acids are mainly divided into three types:
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) – found primarily in plant oils such as flaxseed and chia oil.
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) – found mainly in fatty fish and seafood.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – also present in fish and seafood, and especially important for brain and vision health.
Omega-3s play a crucial role in many important bodily processes – they reduce chronic inflammation associated with cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases, support brain function, improve heart and vascular health, and contribute to good vision and skin condition.
Benefits and Mechanisms of Action
Omega-3 fatty acids are structural components of cell membranes and participate in many biological functions. They affect:
Inflammation and the Immune System
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA, play a key role in regulating inflammatory processes in the body. They reduce the synthesis of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes, making them effective in relieving chronic inflammation associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular issues. They also aid recovery after physical injuries and exertion by reducing localized inflammation and pain.
This ability to regulate inflammation also positively affects the immune system. Omega-3s influence the activity of key immune cells – macrophages, dendritic cells, and T-lymphocytes – and promote a balanced, rather than excessive, immune response. This is especially important for preventing autoimmune reactions and maintaining normal resistance to viruses and bacteria.
Some studies show that regular intake of omega-3 fatty acids may even improve the body’s response to vaccines and speed up recovery from infections. For example, research has found that omega-3 supplements increase the production of certain immune cells and antibody responses after vaccination.
Another study conducted by the University of Rochester shows that omega-3 derivatives are effective in eliminating the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae, commonly found in chronic inflammatory diseases such as COPD.
Cardiovascular System
Omega-3 fatty acids have a proven positive effect on the cardiovascular system. They help dilate blood vessels and improve circulation, which can lead to a moderate reduction in blood pressure. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), a daily intake of about 3 grams of EPA/DHA can have a noticeable effect on lowering blood pressure.
The most pronounced effect of Omega-3s is seen on triglyceride levels, which can decrease by up to 25–30% with higher doses (2–4 g daily). This is a key factor in reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Regarding LDL cholesterol (the so-called “bad” cholesterol), Omega-3s may slightly increase its levels in some people. However, it’s important to note that this increase is often due to an enlargement of LDL particle size – larger particles are less atherogenic (i.e., less harmful to arteries) compared to small, dense LDL.
Additionally, EPA and DHA improve endothelial function (the inner lining of blood vessels), reduce inflammation, and inhibit clot formation. This further contributes to protection against heart attacks and strokes.
Brain Function
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a key component of Omega-3s, is essential for brain health, making up a large part of brain cells and playing a vital role in cognitive functions, memory, and mental health. Omega-3 fatty acids help build cell membranes in the brain and facilitate communication between neurons, which is crucial for concentration and preventing age-related cognitive decline. DHA deficiency is linked to an increased risk of depression and cognitive difficulties, and studies show that Omega-3s can improve working memory, attention, and focus.
Joint Health
Omega-3s have strong anti-inflammatory properties, making them very useful in treating joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. They reduce joint inflammation, relieve pain and stiffness, and improve mobility and flexibility. Additionally, Omega-3s help strengthen cartilage and slow the progression of age-related joint disorders.
Skin Health
Omega-3 fatty acids support the maintenance of the skin barrier, hydration, and elasticity. They reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are often at the root of skin problems like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Taking Omega-3s contributes to smoother skin, less redness, and increased resistance to environmental damage, including UV rays.
Hormonal Balance
Hormonal balance is also influenced by these fatty acids. They help regulate hormone levels related to inflammation and metabolism and alleviate symptoms of various hormonal disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and menopause. Omega-3 fatty acids help stabilize insulin levels and improve fat metabolism, leading to better overall health.
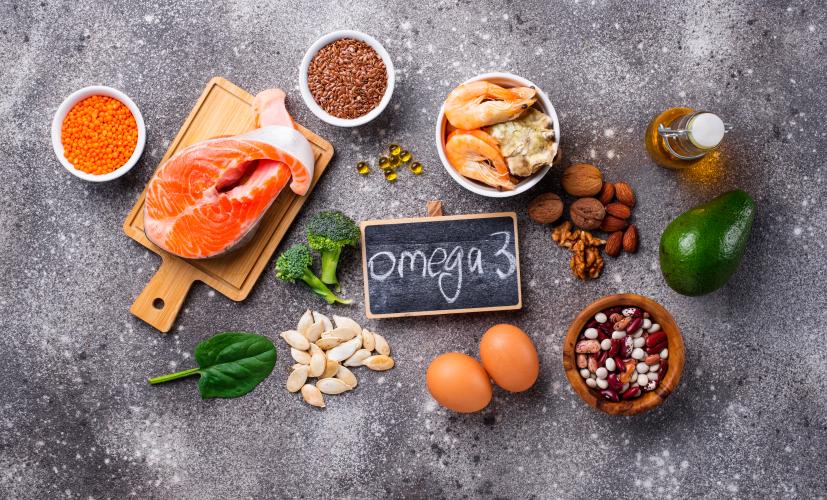
What Are the Best Sources of Omega-3?
The richest dietary sources of Omega-3 include:
Fatty fish – salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna
Seafood – shrimp, mussels, caviar
Plant oils – flaxseed oil, chia oil, walnut oil
Nuts and seeds – walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds
Eating fish at least twice a week is an excellent way to maintain a good balance of Omega-3 fatty acids in the body.
How to Choose the Right Omega-3 Supplement
If you're not getting enough Omega-3 through food, you can include dietary supplements. When choosing the right product, it’s important to consider the following factors:
EPA and DHA ratio – supplements with higher levels of these two acids offer greater health benefits.
Source of Omega-3 – fish oil extracted from small fish (anchovies, sardines), as they contain fewer heavy metals than larger predatory species.
Purification method – quality supplements undergo molecular distillation to remove contaminants.
Form of Omega-3 – our bodies absorb supplements better when they are in triglyceride form rather than the more common ethyl ester form. Therefore, it’s best to choose supplements with triglycerides.
How Much Omega-3 Can Be Taken Daily
There is no established specific recommendation for total Omega-3 fatty acid intake, except for ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). The amount of ALA the body needs daily depends mainly on age and gender. According to data from the National Institutes of Health, the table below shows the recommended intake for different age groups:
Age
Recommended ALA Intake
0–12 months 0.5 g
Children 1–3 years 0.7 g
Children 4–8 years 0.9 g
Boys 9–13 years 1.2 g
Girls 9–13 years 1.0 g
Boys 14–18 years 1.6 g
Girls 14–18 years 1.1 g
Men 1.6 g
Women 1.1 g
Pregnant women 1.4 g
Breastfeeding women 1.3 g
Excessive intake of Omega-3 may lead to unwanted effects such as blood thinning and increased risk of bleeding.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are not just another supplement on the vitamin shelf – they are a fundamental element for maintaining balance and harmony in the body. By including them in your daily diet, you support your body in fighting chronic diseases and contribute to a better quality of life. This is not just a temporary boost, but a way to stay energetic and mentally sharp for years to come.
So, whether you get them through a varied and balanced diet or with the help of quality supplements, Omega-3s are a reliable partner for your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between Omega-3, Omega-6, and Omega-9?
Omega-3, 6, and 9 are different types of fatty acids. Omega-3 and Omega-6 are essential, meaning the body cannot produce them on its own and they must be obtained through food. Omega-9 is not essential because the body can synthesize it. It’s important to maintain a balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6, as excessive intake of Omega-6 (common in modern diets) can have an inflammatory effect.
Can Omega-3 be taken every day?
Yes, at the recommended daily dose, daily intake of Omega-3 is safe and even recommended for maintaining health.
Is Omega-3 suitable for children?
Yes, Omega-3 is especially important for brain and vision development in children. There are special children’s formulas tailored to age and nutritional needs. However, it’s best to consult a pediatrician before starting supplementation.